Bunion Treatment in Northern New Jersey
 Bunions grow slowly over time. While many patients feel no symptoms from their bunion, others may feel discomfort while walking, wearing certain shoes, and during other activities. These patients require prompt bunion treatment to get them back out to do what they love.
Bunions grow slowly over time. While many patients feel no symptoms from their bunion, others may feel discomfort while walking, wearing certain shoes, and during other activities. These patients require prompt bunion treatment to get them back out to do what they love.
With a team of more than 40 board-certified physicians, nurses, and highly trained staff, Bergen Medical Associates offers a variety of medical services, including podiatry, throughout northern New Jersey.
What Is a Bunion?
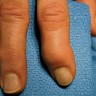
Bunions (also called hallux valgus) occur when excess pressure is put on the big toe. This causes it to align inward, creating a bump at the base of the big toe called a bunion. This bump is where the unaligned metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint protrudes as the big toe curves toward the others. Bunions typically develop in adults, but adolescent patients can also get them.
Bunions develop slowly, creating a growth inside the foot to accommodate the missing space as toe joints bend and grow at a curve. This creates a prominent, bony bump that can lead to painful symptoms. Sometimes, bunions can cause big toes to cross over other toes permanently. Bunions can also become irritated and inflamed, which causes painful symptoms to occur. These deformities can worsen over time, so patients require prompt treatment.
What Are the Types of Bunions?
Bunions stemming from excess pressure on the toes are the most common type. However, bunions may appear on toes for a variety of other reasons. The type of bunion a patient has depends on how they developed it. Types of bunions include:
Tailor’s Bunion (Bunionettes)
Tailor’s bunions are caused by wearing shoes that do not fit comfortably. Instead of growing at the base of the big toe, bunionettes grow on the base of the pinky toe. Excess pressure causes pinky toes to curve inward, messing with proper toe alignment.
Congenital Bunions
Some patients may be born with bunions. These bunions usually are inherited and may be associated with a genetic or neuromuscular condition.
Juvenile or Adolescent Bunions
Adolescent bunions occur in patients younger than 18, typically in female patients ages 10 through 15. Usually, juvenile bunions do not cause an inability to move the big toe. However, they can still cause painful symptoms.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Bunions?
Because bunions cause misalignment with foot joints, they can also lead to uncomfortable symptoms, such as:
- Numbness in or around the affected toe
- Stiffness
- Pain
- Painful, tight tendons and joints in toes (called hammertoes)
- Swelling
- Inability to wear certain types of shoes
- Redness or discoloration
- Worsening discomfort when wearing shoes
- Difficulty bending or moving the big toe
- Hardened skin on the bottom of the foot
- Corn or callus that grows on the bump
What Are the Causes and Risk Factors?
Bunions most commonly form when patients regularly wear uncomfortable shoes too small for their feet. This is especially true for women wearing heels and other narrow-toed shoe types. When patients continue wearing the same styles of shoes, their toes naturally curve and grow inward as they push into each other and squeeze together. This is how bunions form and uncomfortable symptoms arise. Bunions grow to make up for the misalignment in toe joints.
However, bunions can occur for a variety of other reasons. If a patient has a family history of bunions, they are more likely to develop them in the future. Patients born with a naturally abnormal bone structure in their feet may also experience bunions. The way a patient walks, as well as standing for long periods and working on their feet, can also contribute to the formation of bunions.
In addition, certain health conditions that increase inflammation, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the likelihood of bunion growth. Plantar fasciitis is another inflammatory disease that occurs when patients have inflammation in the plantar fascia, the thick tissue at the bottom of the foot. This tissue helps with foot movement and walking. Plantar fasciitis can contribute to a future bunion diagnosis. Patients with an extensive foot injury history (like athletes) are also prone to bunions.
How Do You Diagnose a Bunion?
To diagnose a bunion, patients must visit a podiatrist. During initial appointments, podiatrists simply complete a physical examination of the foot and bunion. They may also ask patient questions regarding their symptoms and medical history. Patients should inform their physician if their bunion causes discomfort during certain activities, as well as when they first noticed the bunion. Physicians may order additional diagnostic testing, such as foot X-rays, to check how misaligned the MTP joint is.
Bunion Treatment at Bergen Medical Associates
Patients diagnosed with bunions cannot treat them on their own and must visit a podiatrist for an official diagnosis and treatment. Treatment is essential for avoiding more serious complications in the future, like osteoarthritis, bursitis, and hammertoes.
Bunion treatments are typically conservative and easy, requiring patients to make lifestyle changes or wear devices that alleviate discomfort. For example, if bunions develop because a patient’s shoes are too small to fit their feet, they must switch to shoes that fit better. This helps relieve excess pressure on the big toe. Patients can also stretch shoes they already own to make more room for their toes.
Patients may also need to purchase bunion pads and taping, which they can find over the counter. These pads cushion the bunion against shoes, relieving discomfort and pressure. Patients can also consider taping their toes with medical tape to hold them in the proper position. Physicians may suggest that patients get orthotic shoe inserts or other devices for additional foot support.
If a patient experiences discomfort from their bunion, podiatrists may prescribe medications. Patients should also ice their feet to help with painful symptoms. In some cases, patients may undergo physical therapy to strengthen the foot. During physical therapy, patients complete light exercises to promote proper toe alignment.
If conservative treatments do not alleviate a patient’s symptoms, they may require bunion correction surgery. This treatment is reserved for serious bunion cases that cause a patient severe pain. Podiatrists will inform patients if this is the best course of treatment.
Find Comprehensive Medical Care at Bergen Medical Associates
Patients can find comprehensive medical treatments for bunions and other conditions at Bergen Medical Associates. We serve patients at locations across northern New Jersey. We offer a wide range of specialties at each location, making healthcare convenient for the community. To learn more about bunion treatment and other podiatry services, contact Bergen Medical Associates today.